Global Register Allocation: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(Created page with "{{DISPLAYTITLE:Global Register Allocation (Register Allocation)}} == Description == Register allocation is the process of mapping the unlimited number of symbolic registers assumed in the intermediate language into the limited real machine registers. Global register allocation deals with the allocation of registers in code containing branches (http://www.cs.ucr.edu/~gupta/research/Publications/Comp/p370-gupta.pdf). == Related Problems == Related: Local Register A...") |
No edit summary |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
== Parameters == | == Parameters == | ||
$n$: number of live ranges (the number of candidates to reside in registers) | |||
== Table of Algorithms == | == Table of Algorithms == | ||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
| [[Cooper and Dasgupta algorithm ( Register Allocation)|Cooper and Dasgupta algorithm]] || 1983 || $O(n^{2})$ || || Exact || Deterministic || | | [[Cooper and Dasgupta algorithm ( Register Allocation)|Cooper and Dasgupta algorithm]] || 1983 || $O(n^{2})$ || || Exact || Deterministic || | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[Optimal Register Allocation (ORA), Goodwin & Wilken Algorithm (Global Register Allocation Register Allocation)|Optimal Register Allocation (ORA), Goodwin & Wilken Algorithm]] || 1996 || $O(n^{3})$ || Depends on the choice of {0}-{1} ILP solver || Exact || Deterministic || [https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi | | [[Optimal Register Allocation (ORA), Goodwin & Wilken Algorithm (Global Register Allocation Register Allocation)|Optimal Register Allocation (ORA), Goodwin & Wilken Algorithm]] || 1996 || $O(n^{3})$ || Depends on the choice of {0}-{1} ILP solver || Exact || Deterministic || [https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/(SICI)1097-024X(199608)26:8%3C929::AID-SPE40%3E3.0.CO;2-T Time] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[Kong and Wilken Algorithm (Global Register Allocation Register Allocation)|Kong and Wilken Algorithm]] || 1998 || $O(n^{3})$ || ? Probably also dependent on the ILP solver || Exact || Deterministic || [https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.5555/290940.291002 Time] | | [[Kong and Wilken Algorithm (Global Register Allocation Register Allocation)|Kong and Wilken Algorithm]] || 1998 || $O(n^{3})$ || ? Probably also dependent on the ILP solver || Exact || Deterministic || [https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.5555/290940.291002 Time] | ||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
|} | |} | ||
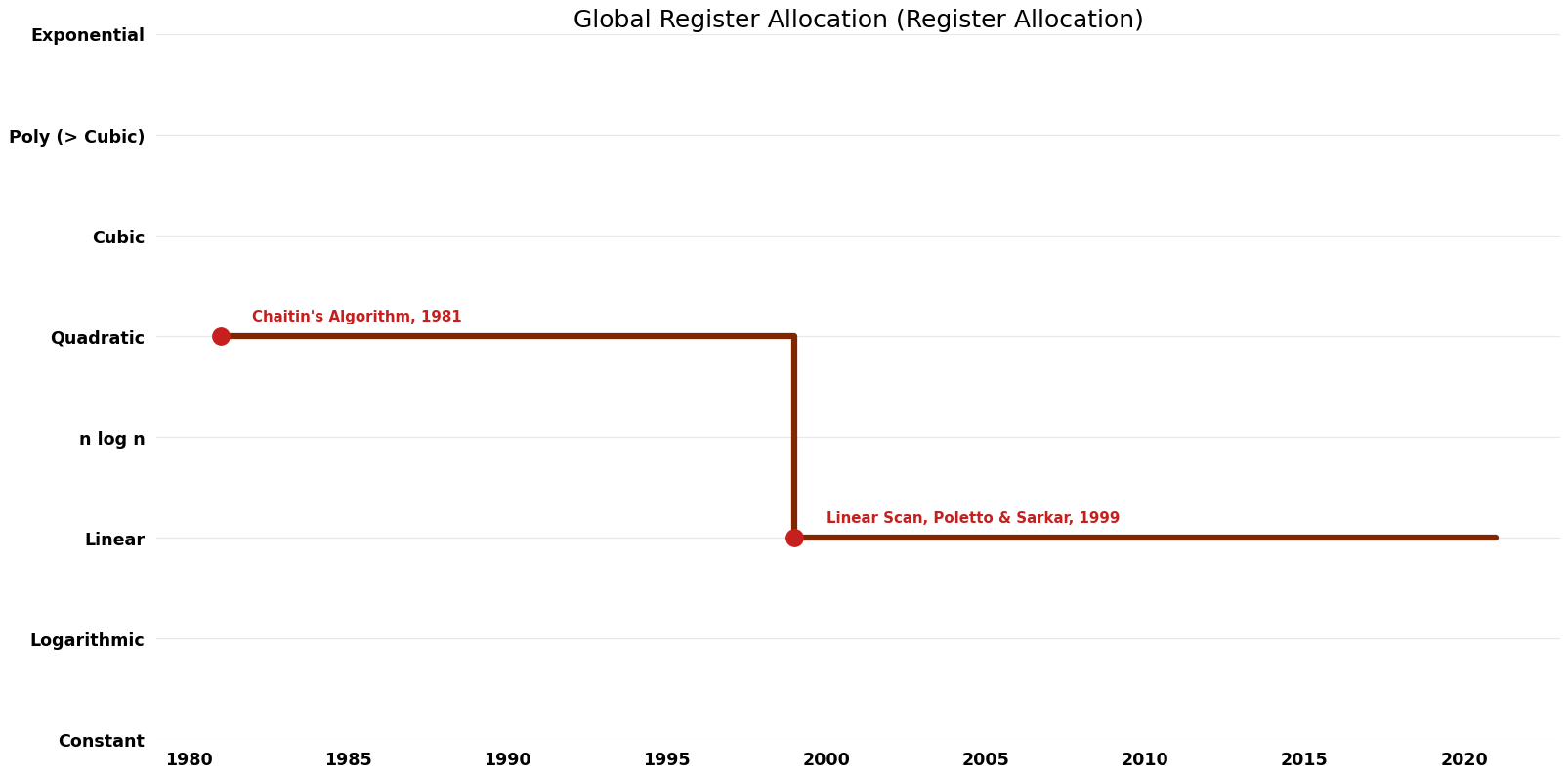
== Time Complexity | == Time Complexity Graph == | ||
[[File:Register Allocation - Global Register Allocation - Time.png|1000px]] | [[File:Register Allocation - Global Register Allocation - Time.png|1000px]] | ||
== References/Citation == | == References/Citation == | ||
http://www.cs.ucr.edu/~gupta/research/Publications/Comp/p370-gupta.pdf | http://www.cs.ucr.edu/~gupta/research/Publications/Comp/p370-gupta.pdf | ||
Latest revision as of 09:08, 28 April 2023
Description
Register allocation is the process of mapping the unlimited number of symbolic registers assumed in the intermediate language into the limited real machine registers.
Global register allocation deals with the allocation of registers in code containing branches (http://www.cs.ucr.edu/~gupta/research/Publications/Comp/p370-gupta.pdf).
Related Problems
Related: Local Register Allocation
Parameters
$n$: number of live ranges (the number of candidates to reside in registers)
Table of Algorithms
| Name | Year | Time | Space | Approximation Factor | Model | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chaitin's Algorithm | 1981 | $O(n^{2})$ | $O(n^{2})$ | Exact | Deterministic | Time |
| Chow's Algorithm | 1984 | $O(n^{2})$ | $O(n^{2})$ | Exact | Deterministic | Time |
| Linear Scan, Poletto & Sarkar | 1999 | $O(n)$ | $O(r)$ | Exact | Deterministic | Time |
| Cooper and Dasgupta algorithm | 1983 | $O(n^{2})$ | Exact | Deterministic | ||
| Optimal Register Allocation (ORA), Goodwin & Wilken Algorithm | 1996 | $O(n^{3})$ | Depends on the choice of {0}-{1} ILP solver | Exact | Deterministic | Time |
| Kong and Wilken Algorithm | 1998 | $O(n^{3})$ | ? Probably also dependent on the ILP solver | Exact | Deterministic | Time |
| Demand-Driven Register Allocation | 1996 | $O(n^{2})$ | $O(n^{2})$ | Exact | Deterministic | Time |
Time Complexity Graph
References/Citation
http://www.cs.ucr.edu/~gupta/research/Publications/Comp/p370-gupta.pdf