Steal, No-Force: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(Created page with "{{DISPLAYTITLE:Steal, No-Force (Recovery)}} == Description == Recovery is the process of reverting back to a safe state prior to a system failure. With a Steal/No-Force policy, the recovery algorithm will write possibly uncommited data to memory, while not forcing all commits to memory. == Related Problems == Related: No-Steal, Force == Parameters == $n$: number of transactions before crash == Table of Algorithms == {| class="wikitable sortable" style="t...") |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
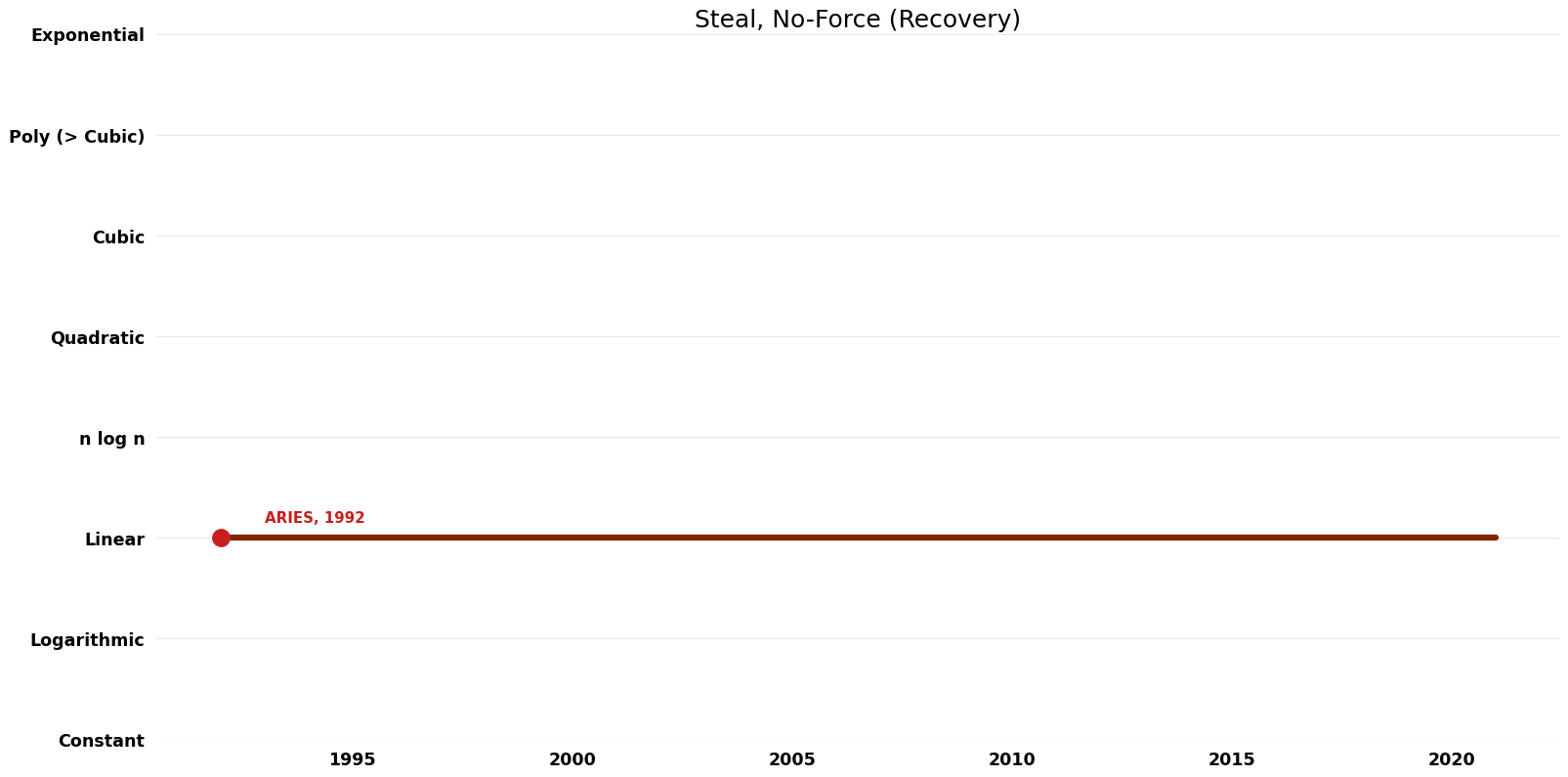
== Time Complexity Graph == | |||
[[File:Recovery - Steal, No-Force - Time.png|1000px]] | |||
== References/Citation == | == References/Citation == | ||
https://dl.acm.org/doi/pdf/10.1145/128765.128770 | https://dl.acm.org/doi/pdf/10.1145/128765.128770 | ||
Latest revision as of 10:12, 28 April 2023
Description
Recovery is the process of reverting back to a safe state prior to a system failure.
With a Steal/No-Force policy, the recovery algorithm will write possibly uncommited data to memory, while not forcing all commits to memory.
Related Problems
Related: No-Steal, Force
Parameters
$n$: number of transactions before crash
Table of Algorithms
| Name | Year | Time | Space | Approximation Factor | Model | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ARIES | 1992 | $O(n)$ | $O(n)$? | Exact | Deterministic | Time |